Your tongue plays a more important role than just helping with speech and taste—it can serve as a window to your overall health. Changes in its color, texture, or appearance may indicate underlying health conditions that deserve attention. In this article, we explore four common tongue symptoms, their possible causes, how to care for them, and when to seek medical help.
1. White Coating on the Tongue
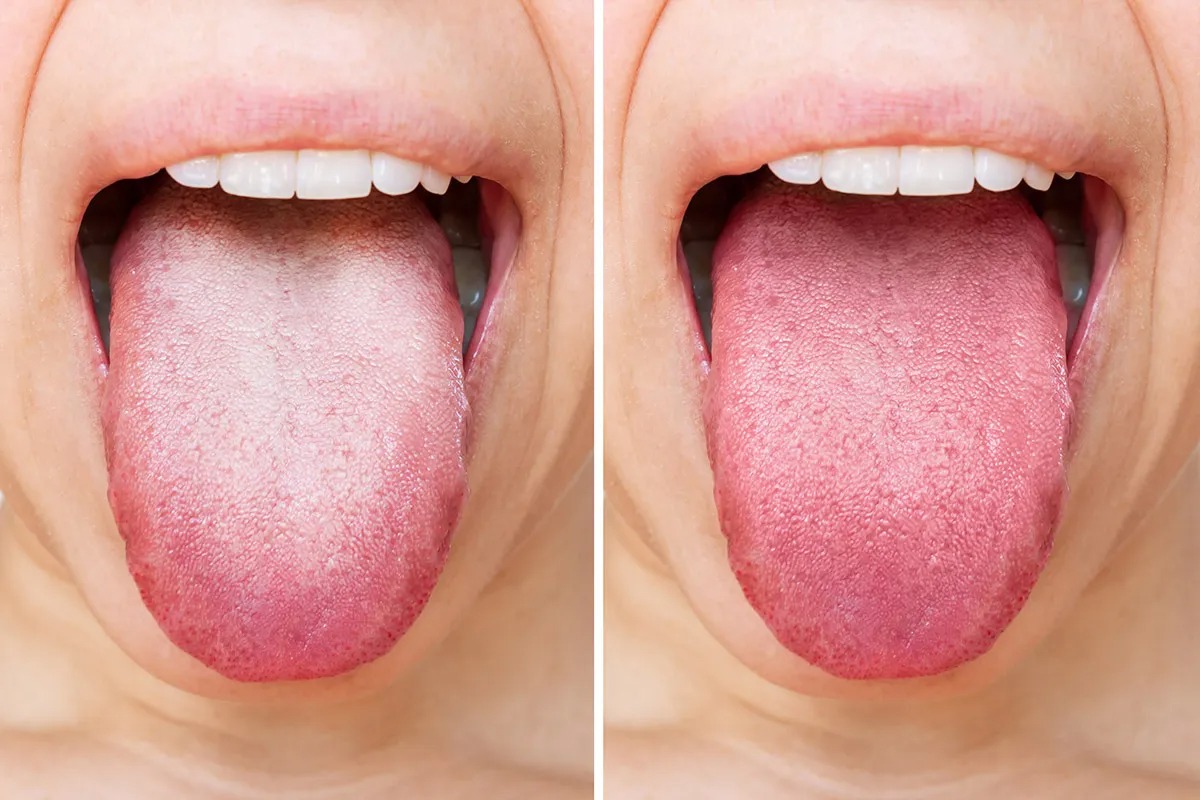
Possible Cause: Oral Thrush (Candidiasis)
A white or yellowish coating on the tongue can be a sign of oral thrush, a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans. This yeast naturally exists in the mouth, but certain conditions can lead to an imbalance and subsequent infection.
Common Causes:
-
Poor oral hygiene
-
Antibiotic use, which disrupts healthy bacteria
-
A weakened immune system (e.g., in people with diabetes or HIV/AIDS)
-
Smoking or dry mouth
Symptoms:
-
Thick white or yellow patches on the tongue or inner cheeks
-
Slight burning or soreness
-
A metallic or unpleasant taste
-
Bad breath
Prevention and Home Care:
-
Brush your teeth and
clean your tongue twice daily
-
Rinse your mouth with
saltwater or baking soda solution
- Avoid sugary and yeast-rich foodsthat can feed the fungus
-
Incorporate
probiotic-rich foodslike yogurt and kefir
-
Stay well-hydrated and maintain good dental hygiene
When to See a Doctor:
If the white patches persist for more than a week, or if you experience pain, see your dentist or healthcare provider. Antifungal treatments may be required for moderate to severe cases.
2. Red, Bald, and Glossy Tongue
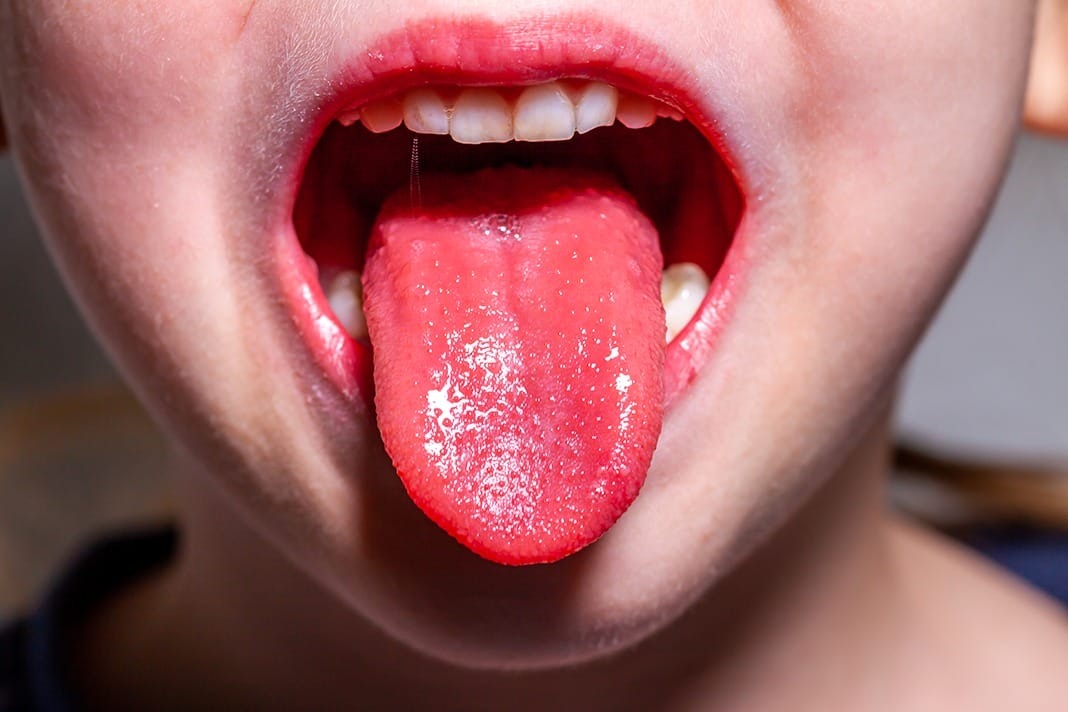

Possible Cause: Vitamin Deficiency (B12, Iron, or Folate)
A smooth, reddish tongue that appears bald or shiny may be a sign of vitamin deficiency, particularly vitamin B12, iron, or folate (B9). These nutrients are essential for healthy red blood cells and nerve function.
Common Causes:
-
Poor dietary intake of B12 (common in vegetarians/vegans)
-
Absorption issues like
pernicious anemiaorceliac disease
-
Chronic alcohol consumption
-
Long-term use of antacids or metformin
Symptoms:
-
Tongue appears red, smooth, and shiny
-
Burning sensation, especially when eating spicy or acidic foods
-
Fatigue, pale skin, or dizziness (symptoms of anemia)
Prevention and Home Care:
- Eat iron-rich foodslike red meat, spinach, and legumes
-
Include sources of
vitamin B12such as eggs, dairy, poultry, and fish
- Consider B-complex supplementsafter consulting a doctor
-
Reduce alcohol intake and avoid irritating foods if discomfort persists
If symptoms include neurological changes like tingling or memory issues, seek medical attention as B12 deficiency can lead to irreversible damage if untreated.
3. Cracked or Fissured Tongue
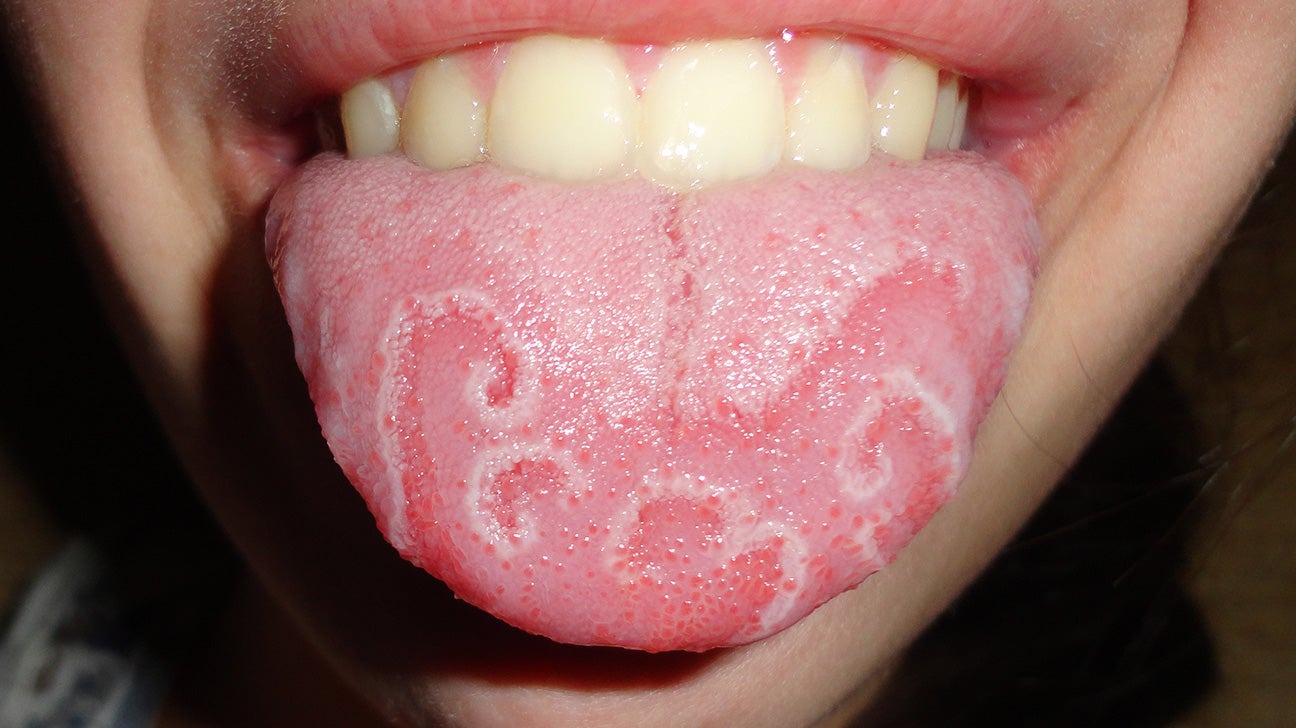
Possible Cause: Fissured Tongue or Geographic Tongue
A fissured tongue presents with deep grooves, often resembling cracks across the surface. It may be inherited or associated with conditions such as psoriasis or Down syndrome. A related condition, geographic tongue, displays irregular patches that change over time.
Common Causes:
-
Genetics (runs in families)
-
Nutritional deficiencies
-
Dehydration
-
Skin conditions like psoriasis or lichen planus
Symptoms:
-
Visible cracks or deep grooves on the tongue
-
Typically painless unless debris or food particles become trapped
-
“Map-like” appearance in geographic tongue
Prevention and Home Care:
-
Use a
soft toothbrushto gently clean the tongue and remove trapped particles
- Drink plenty of waterto stay hydrated
- Avoid spicy, acidic, or salty foodsif discomfort occurs
Generally, a fissured tongue is harmless and doesn’t require medical treatment unless accompanied by pain or secondary infections.
4. Purple or Dark-Colored Tongue

Possible Cause: Circulatory Issues, Cyanosis, or Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) Deficiency
A purplish or bluish tongue may signal reduced oxygen circulation (a condition known as cyanosis) or a possible vitamin B2 deficiency. In some cases, it can also occur temporarily due to cold weather or certain foods.
Common Causes:
-
Cold exposure or vasoconstriction
-
Respiratory problems such as
asthmaorCOPD
-
Cardiovascular issues like heart failure
-
Deficiency of riboflavin (vitamin B2)
Symptoms:
-
Purple, blue, or dark discoloration of the tongue
-
Cold hands and feet
-
Dizziness or fatigue
-
Breathing difficulties (in severe cases)
Prevention and Home Care:
- Dress warmlyand avoid prolonged exposure to cold environments
-
Perform
light exerciseto improve circulation
-
Eat riboflavin-rich foods: eggs, almonds, dairy, green vegetables
-
Monitor for
shortness of breath or fatigue—seek medical advice if these symptoms appear
If a purple tongue appears suddenly and is accompanied by chest pain or breathing difficulties, seek immediate medical attention.
When to See a Doctor
While many tongue symptoms are harmless or temporary, it’s crucial to seek medical care if any of the following occur:
-
The symptom lasts
longer than 1–2 weeks
-
Tongue becomes
painful, swollen, or changes rapidly
- Difficulty eating, speaking, or breathing
-
Accompanied by
fever, fatigue, or other systemic symptoms
An early diagnosis can help prevent complications and ensure proper treatment.
General Oral and Tongue Health Tips
Maintaining a clean, healthy tongue is part of overall oral hygiene. Here are some daily practices:
- Brush your tongue gentlywith a toothbrush or use a tongue scraper
- Stay hydratedto avoid dry mouth and promote a healthy oral environment
- Limit smoking and alcohol, which can lead to tongue discoloration or oral infections
- Visit your dentist every 6 monthsfor regular check-ups and professional cleanings
Final Thoughts
Your tongue can reveal valuable clues about your health. From white coatings to color changes, these signs should not be ignored. By staying informed and maintaining good oral hygiene, you can detect early warning signs of nutritional deficiencies, infections, or even systemic illnesses.
If you notice persistent or unusual tongue symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.