Polymyalgia Rheumatica and Psoriasis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
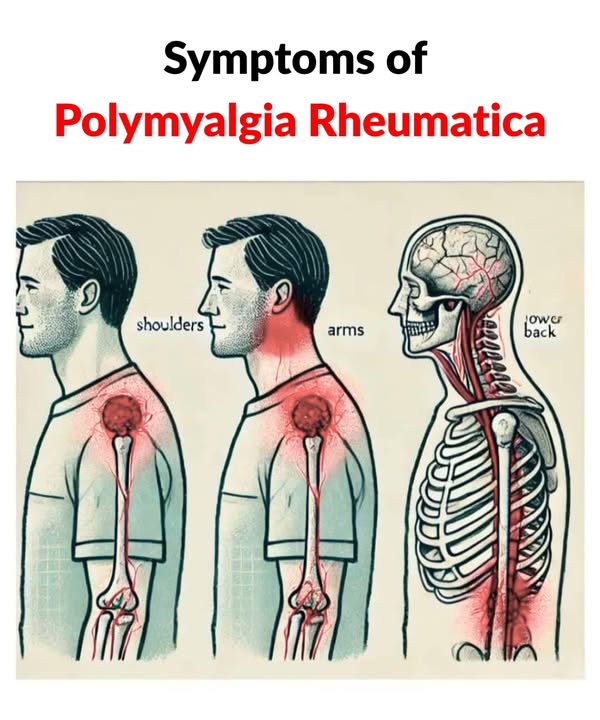
Polymyalgia rheumatica is an inflammatory condition with muscle and joint stiffness. It mainly affects the hips and shoulders, and symptoms can start suddenly or gradually over days. It rarely affects those under 50 and is common in people over 65. Here are some key symptoms:
- Shoulder Pain
It usually starts with aching in the shoulders. This makes daily tasks like dressing or reaching for things difficult. The pain is often on both sides and gets worse at night, making it hard to sleep. - Pain in Other Areas
Besides the shoulders, many people also have pain in other major muscle groups, such as the hips, upper arms, buttocks, thighs, and neck. The deep pain worsens after repetitive tasks or long periods of inactivity. - Stiffness
A major sign is extreme stiffness, especially in the morning or after being inactive. Even sitting in one position for a while can make the body parts stiff and moving uncomfortable. - Limited Range of Motion
If untreated, the stiffness can limit movement. For example, the shoulders ache when moved beyond a certain range, making it hard to raise or extend the arms. It can also weaken hip mobility, making activities like getting up or climbing stairs tough. - Knee, Elbow, and Wrist Pain
While most have hip and shoulder pain, some also have stiffness in the knees, elbows, and wrists. Wrist pain makes writing or typing difficult, and knee pain can make walking a struggle.
As we age, our bodies are more prone to such conditions. If you or a loved one shows these signs, consult a healthcare provider.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide. It’s not contagious, but early symptom recognition is key for effective management.
- Types of Psoriasis
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common, with red patches covered in silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Characterized by small, drop-shaped spots, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Has red, inflamed skin with pus-filled blisters.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Appears in moist areas like skin folds, with shiny, red lesions.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare and severe form causing widespread redness, peeling, and a burning sensation, which is a medical emergency.
- Causes
Psoriasis is due to an immune system problem where T-cells wrongly attack healthy skin cells, causing rapid skin cell turnover. Genetic factors are important, and triggers include excessive alcohol, infections, and certain medications like beta-blockers or lithium. - Diagnosis and Treatment
A dermatologist usually diagnoses it through a physical exam, and sometimes a skin biopsy. There’s no cure, but treatments can manage symptoms:- Topical treatments: Corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light.
- Systemic treatments: Oral or injectable medications for severe cases.
If you notice persistent skin problems like red patches, scaling, or rashes, see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Understanding psoriasis and its triggers helps you take control of your skin health. Don’t ignore the signs—get medical advice.