Skin irritation in the groin area is a common concern that can affect people of all genders and ages. The groin area is a warm, moist, and often closed environment, making it prone to various dermatological problems. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and safe treatments for these conditions is essential for maintaining good hygiene and skin health
Buy vitamins and supplements
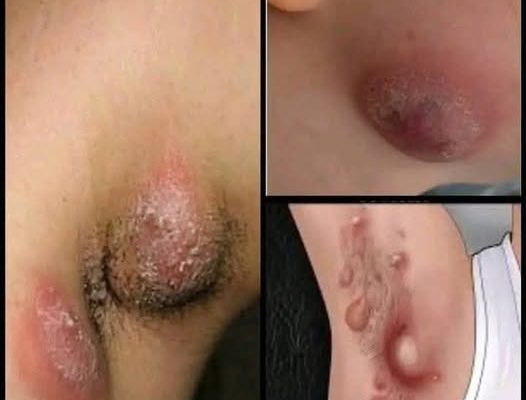
1. Ingrown hairs
What are they?
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair curls backward or grows sideways into the skin instead of up. This often causes itchy, pimple-like red bumps. In some cases, ingrown hairs can become infected, resulting in painful, pus-filled lesions.
Causes
- Shaving, waxing, or plucking hair too close
- Wearing tight clothing that causes friction
- Naturally curly or thick hair
Symptoms
- Small round bumps that may contain pus
- Redness and inflammation
- Itching or discomfort in the affected area
Treatment
- Apply a warm compress to reduce swelling.
- Use exfoliating cleansers to remove dead skin.
- Avoid shaving until the area heals.
- In severe cases, consult a dermatologist.
Source: American Academy of Dermatology
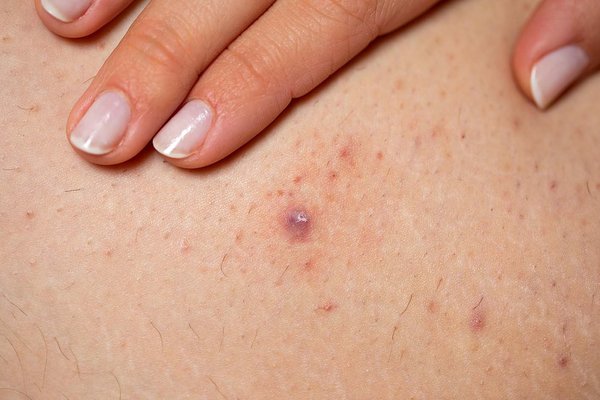
2. Folliculitis
What is
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles caused by bacteria, fungus, or irritation. It appears as red or white bumps around the hair follicles and can be itchy or painful.
Causes
- Bacterial infections, especially Staphylococcus aureus
- Friction from tight clothing
- Shaving or waxing
- Exposure to hot tubs or poorly disinfected water
Symptoms
- Red, inflamed bumps or pustules
- Mild burning or itching
- Sensitive skin around hair follicles
Treatment
- Clean the area with antibacterial soap.
- Apply over-the-counter antibiotic ointments.
- Use warm compresses
- In persistent or severe cases, oral antibiotics may be required.
Source: Mayo Clinic
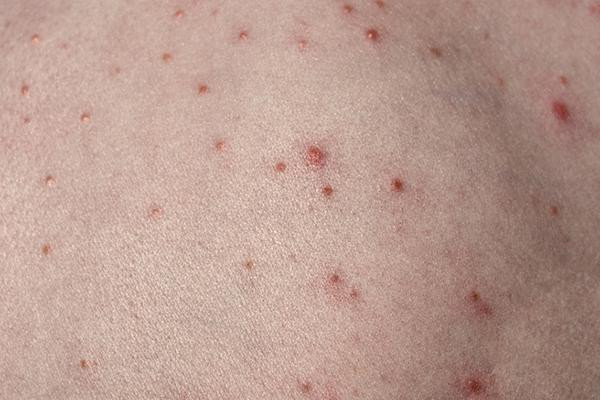
3. Jock itch (tinea cruris)
What is
Jock itch, commonly known as ringworm, is a fungal infection that affects the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. It’s most common in men, but can affect anyone. The infection thrives in warm, humid environments.
Causes
- excessive sweating
- Wear tight or non-breathable clothing
- Sharing towels or personal items
- Poor hygiene
Symptoms
- Red, scaly patches with raised edges
- Itching, burning, or irritation in the groin.
- Rash that may spread to the thighs or buttocks
Treatment
- Use antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or terbinafine.
- Keep the area clean and dry.
- Avoid sharing personal items
- Wear loose, breathable underwear.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
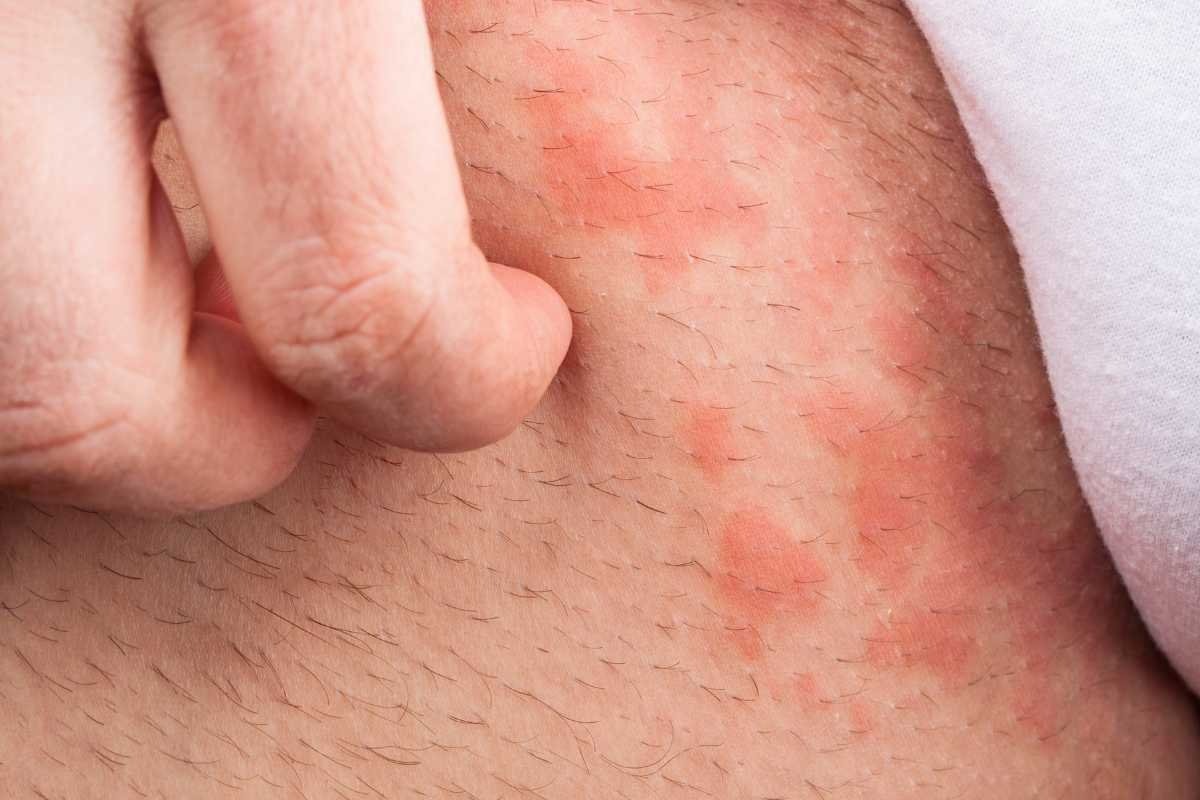
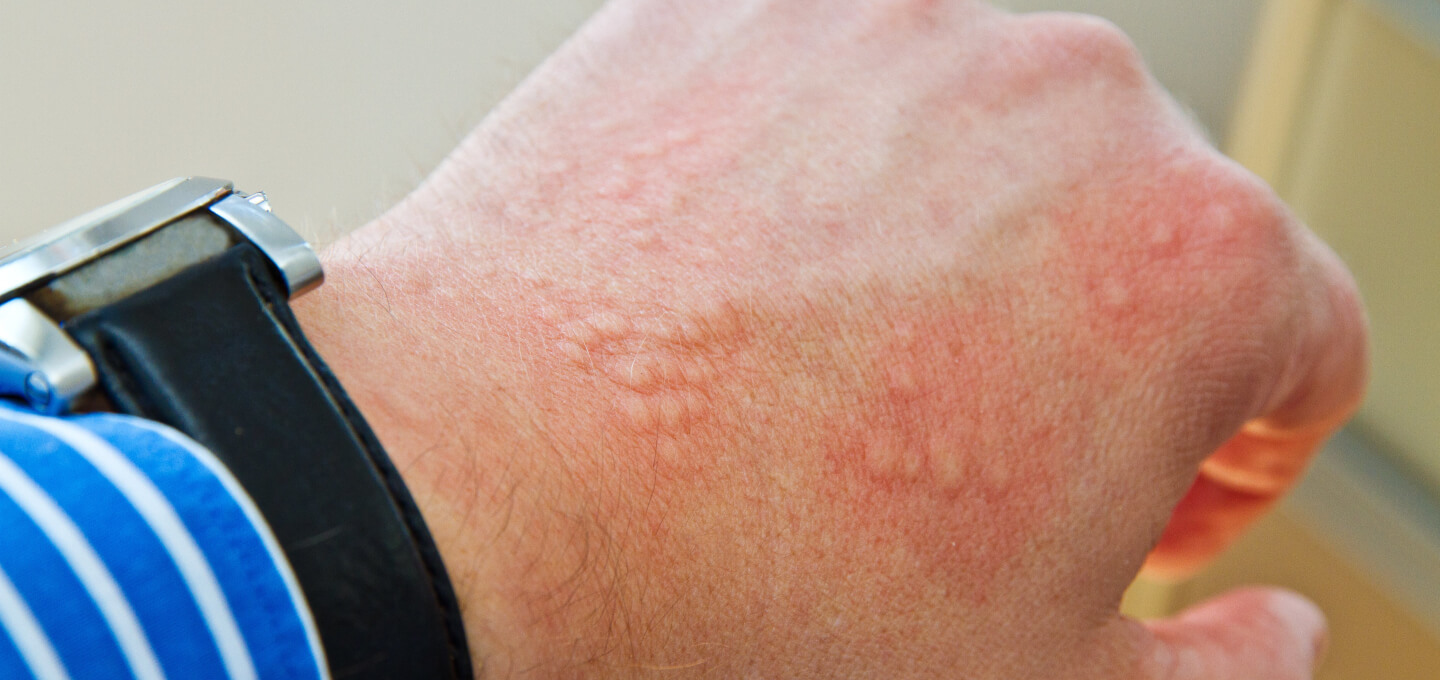
4. Contact dermatitis
What is
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to an allergen or irritant. This reaction can be caused by detergents, soaps, synthetic fabrics, or body lotions.
Causes
- Allergic reactions to perfumes, dyes, or latex.
- Irritation from tight or unwashed clothing
- Prolonged exposure to sweat or moisture.
Symptoms
- Red, swollen, or itchy spots
- flaking or peeling of the skin
- Small blisters in some cases
Treatment
- Avoid known irritants or allergens.
- Use fragrance-free moisturizers
- Apply hydrocortisone cream to relieve itching.
- Consult a dermatologist if symptoms persist.
Source: Cleveland Clinic
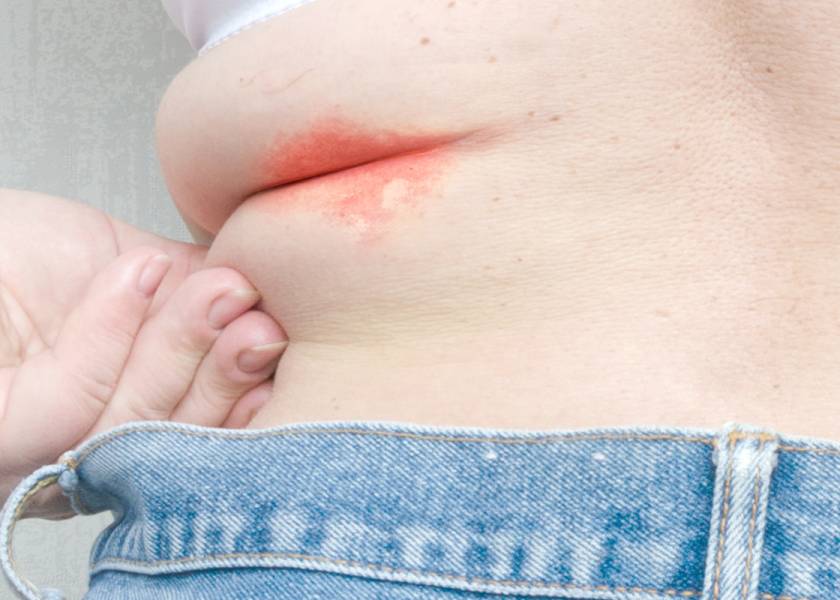
5. Intertrigo
What is
Intertrigo is a skin rash that occurs in skin folds, including the groin. It is caused by friction, moisture, and poor air circulation.
Causes
- excessive sweating
- Friction between skin folds
- Obesity or overweight
- Wear tight-fitting, non-breathable clothing
Symptoms
- Red and raw skin
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Bad smell from the affected area
Treatment
- Keep the area dry with talcum powder or antifungal powder.
- Use protective creams such as zinc oxide.
- Treat any secondary infections with antifungal or antibacterial creams.
Source: Healthline
Preventive tips
Maintaining good hygiene and choosing appropriate skin care habits can go a long way toward preventing groin irritation. Here are some recommended practices:
- Shave carefully: Use a clean, sharp razor and shave in the direction of hair growth. Consider using shaving cream or gel to reduce friction.
- Choose breathable clothing: Wear cotton underwear and avoid tight synthetic fabrics.
- Maintain good hygiene: Wash the area daily and after sweating heavily. Dry thoroughly to prevent the growth of fungus.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Towels, razors, and clothing can carry fungi or bacteria.
- Use fragrance-free products: Harsh chemicals or perfumes can cause contact dermatitis.
When to see a doctor
While many groin-related skin problems can be treated at home, consult a healthcare provider if:
- The rash persists for more than two weeks.
- There is severe pain, swelling, or pus.
- You have a fever or flu-like symptoms.
- The rash spreads rapidly or returns frequently.
A medical professional can accurately diagnose the condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment to prevent complications.
Conclusion
Groin irritation can be uncomfortable, but it’s usually preventable and treatable with proper care. Whether it’s ingrown hairs from shaving or a fungal infection like jock itch, the key is maintaining hygiene, choosing the right clothing, and addressing symptoms promptly. If in doubt, don’t hesitate to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.